AsterNOS-VPP IPSec VPN Configuration Guide
Transform your network into a secure communication highway with enterprise-grade IPSec VPN tunnels. This comprehensive guide walks you through configuring site-to-site VPN connections on AsterNOS-VPP, enabling encrypted data transmission between branch offices and headquarters over public internet infrastructure.
What You’ll Build
By the end of this guide, you’ll have:
✅ Secure site-to-site VPN tunnels protecting data flows between remote networks
✅ IKE (Internet Key Exchange) authentication with industry-standard encryption
✅ Automatic failover capabilities for dynamic IP scenarios (PPPoE)
✅ Production-ready configurations tested and validated
Use Cases:
- Connect branch offices to headquarters securely
- Establish encrypted links between data centers
- Provide secure remote access for distributed teams
- Protect sensitive data traversing public networks
IPSec in AsterNOS-VPP
What is IPSec?
IPSec (Internet Protocol Security) is a protocol suite developed by the IETF for securing IP communications through authentication and encryption. AsterNOS-VPP implements two core IPSec protocols:
- AH (Authentication Header): Provides data integrity and authentication
- ESP (Encapsulation Security Payload): Provides encryption, authentication, and integrity
How IPSec Works in AsterNOS-VPP?
┌─────────────┐ IPSec Tunnel ┌─────────────┐
│ Branch │ ═══════════════════════════► │ Headquarters│
│ Gateway │ ◄═══════════════════════════ │ Gateway │
└─────────────┘ Encrypted over Internet └─────────────┘
10.1.1.0/24 10.1.2.0/24Key Components:
- IKE Phase 1: Establishes a secure control channel
- IKE Phase 2: Negotiates IPSec Security Associations (SAs)
- Data Encryption: Protects actual traffic flows
- NAT Traversal: Handles VPN traffic through NAT devices
Prerequisites
Knowledge Requirements
- Familiarity with AsterNOS-VPP CLI interface
- Understanding of IP routing and subnet design
- Basic knowledge of VPN concepts
Network Information Needed
Before starting, gather these details for both sites:
| Parameter | Description | Example |
| Public IP | WAN interface IP address | 1.1.1.1 |
| LAN Subnet | Protected internal network | 10.1.1.0/24 |
| Pre-shared Key | Shared secret for authentication | test1234 |
| Gateway IP | Next-hop router | 1.1.1.254 |
Supported Encryption Algorithms
IKE Crypto Algorithms: des iv64, des, 3des, rc5, idea, cast, blowfish, 3idea, des iv32, null, aes cbc, aes ctr, aes gcm 16
Integrity Algorithms: none, md5 96, sha1 96, des mac, kpdk md5, aes xcbc 96, md5 128, sha1 160, cmac 96, aes 128 gmac, aes 192 gmac, aes 256 gmac, hmac sha2 256 128, hmac sha2 384 192, hmac sha2 512 256
Diffie-Hellman Groups: none, modp 768, modp 1024, modp 1536, modp 2048, modp 3072, modp 4096, modp 6144, modp 8192, ecp 192, ecp 256, ecp 384, ecp 512, modp 1024 160, modp 2048 224, modp 2048 256
Scenario 1: Basic Site-to-Site IPSec Tunnel
Network Topology
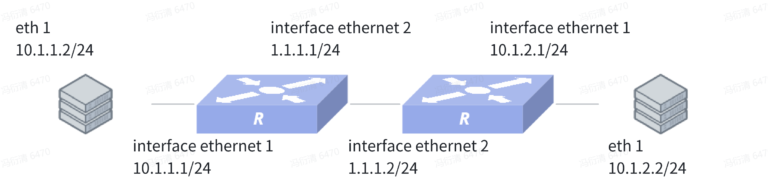
Device 1 Configuration (Branch Gateway)
sonic(config)# interface ethernet 2
sonic(config-if-2)# ip address 1.1.1.1/24
sonic(config-if-2)# ipsec test peer ip4 1.1.1.2
sonic(config-if-2)# mtu 1492
sonic(config)# interface ethernet 1
sonic(config-if-1)# ip address 10.1.1.1/24
sonic(config)# ipsec test
sonic(config-ipsec-test)# shared_key_mic string test1234
sonic(config-ipsec-test)# ike crypto_alg aes-cbc crypto_alg_size 256 integ_alg sha1-96 dh modp-2048
sonic(config-ipsec-test)# ike local type ip4 data 1.1.1.1
sonic(config-ipsec-test)# ike remote type ip4 data 1.1.1.2
sonic(config-ipsec-test)# ike traffic_selector local ip4 addr_start 10.1.1.0 addr_end 10.1.1.255
sonic(config-ipsec-test)# ike traffic_selector remote ip4 addr_start 10.1.2.0 addr_end 10.1.2.255
sonic(config-ipsec-test)# sa crypto_alg aes-cbc crypto_alg_size 256 integ_alg sha1-96
sonic(config-ipsec-test)# sa tunnel ip4 src_ip 1.1.1.1 dst_ip 1.1.1.2 next_hop 1.1.1.2 remote_ip 10.1.2.0/24 shared_interface Ethernet2Device 2 Configuration (Headquarters Gateway)
sonic(config)# interface ethernet 2
sonic(config-if-2)# ip address 1.1.1.2/24
sonic(config-if-2)# mtu 1492
sonic(config)# interface ethernet 1
sonic(config-if-1)# ip address 10.1.2.1/24
sonic(config)# ipsec test
sonic(config-ipsec-test)# shared_key_mic string test1234
sonic(config-ipsec-test)# ike crypto_alg aes-cbc crypto_alg_size 256 integ_alg sha1-96 dh modp-2048
sonic(config-ipsec-test)# ike local type ip4 data 1.1.1.2
sonic(config-ipsec-test)# ike remote type ip4 data 1.1.1.1
sonic(config-ipsec-test)# ike traffic_selector local ip4 addr_start 10.1.2.0 addr_end 10.1.2.255
sonic(config-ipsec-test)# ike traffic_selector remote ip4 addr_start 10.1.1.0 addr_end 10.1.1.255
sonic(config-ipsec-test)# sa crypto_alg aes-cbc crypto_alg_size 256 integ_alg sha1-96
sonic(config-ipsec-test)# sa tunnel ip4 src_ip 1.1.1.2 dst_ip 1.1.1.1 next_hop 1.1.1.1 remote_ip 10.1.1.0/24 shared_interface Ethernet2Do not reboot yet – complete the next step first.
Scenario 2: IPSec with PPPoE (Dynamic IP)
When to Use This Configuration
Use PPPoE + IPSec when:
- Branch office uses DSL/cable internet with DHCP
- WAN IP address changes periodically
- Headquarters has static IP
- Branch must initiate tunnel establishment
Network Topology
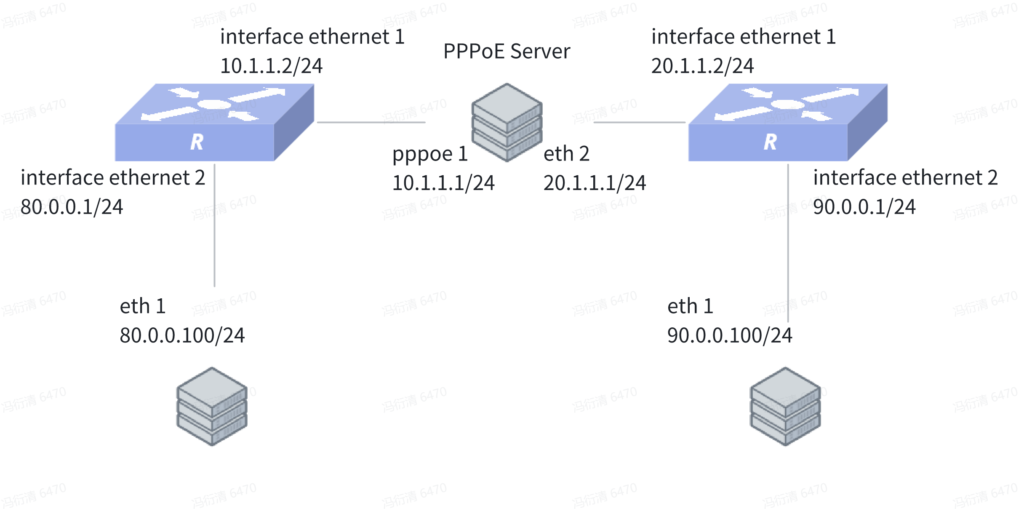
Device 1 Configuration (Branch – PPPoE Client)
sonic(config)# interface dialer 1
sonic(config-dialerif-1)# ppp chap username test1 test123
sonic(config-dialerif-1)# ipsec test peer ip4 20.1.1.2
sonic(config-dialerif-1)# mtu 1492
sonic(config)# interface ethernet 2
sonic(config-if-2)# ip address 80.0.0.1/24
sonic(config)# interface ethernet 1
sonic(config-if-1)# pppoe-client 1
sonic(config)# ipsec test
sonic(config-ipsec-test)# shared_key_mic string test1234
sonic(config-ipsec-test)# ike crypto_alg aes-cbc crypto_alg_size 256 integ_alg sha1-96 dh modp-2048
sonic(config-ipsec-test)# ike local type ip4 data 10.1.1.2
sonic(config-ipsec-test)# ike remote type ip4 data 20.1.1.2
sonic(config-ipsec-test)# ike traffic_selector local ip4 addr_start 80.0.0.0 addr_end 80.0.0.255
sonic(config-ipsec-test)# ike traffic_selector remote ip4 addr_start 90.0.0.0 addr_end 90.0.0.255
sonic(config-ipsec-test)# sa crypto_alg aes-cbc crypto_alg_size 256 integ_alg sha1-96
sonic(config-ipsec-test)# sa tunnel ip4 src_ip 10.1.1.2 dst_ip 20.1.1.2 next_hop 10.1.1.1 remote_ip 90.0.0.0/24 shared_interface Dialer1
sonic(config)# ip route 20.1.1.0/24 dialer 1Device 2 Configuration (Headquarters – Static IP)
sonic(config)# interface ethernet 1
sonic(config-if-1)# ip address 20.1.1.2/24
sonic(config-if-1)# mtu 1492
sonic(config)# interface ethernet 2
sonic(config-if-2)# ip address 90.0.0.1/24
sonic(config)# ipsec test
sonic(config-ipsec-test)# shared_key_mic string test1234
sonic(config-ipsec-test)# ike crypto_alg aes-cbc crypto_alg_size 256 integ_alg sha1-96 dh modp-2048
sonic(config-ipsec-test)# ike local type ip4 data 20.1.1.2
sonic(config-ipsec-test)# ike remote type ip4 data 10.1.1.2
sonic(config-ipsec-test)# ike traffic_selector local ip4 addr_start 90.0.0.0 addr_end 90.0.0.255
sonic(config-ipsec-test)# ike traffic_selector remote ip4 addr_start 80.0.0.0 addr_end 80.0.0.255
sonic(config-ipsec-test)# sa crypto_alg aes-cbc crypto_alg_size 256 integ_alg sha1-96
sonic(config-ipsec-test)# sa tunnel ip4 src_ip 20.1.1.2 dst_ip 10.1.1.2 next_hop 20.1.1.1 remote_ip 80.0.0.0/24 shared_interface Ethernet5
sonic(config)# ip route 10.1.1.0/24 20.1.1.1Key Differences in PPPoE Scenario
| Aspect | Static IP Scenario | PPPoE Scenario |
| Tunnel Initiation | Either side | Branch must initiate |
| IP Address | Both static | Branch dynamic |
| Interface Binding | Physical ethernet | Dialer interface |
| Reconnection | Manual | Automatic on PPPoE reconnect |
Configuration Commands Reference
IPSec Tunnel Creation
sonic(config)# ipsec <name>Creates an IPSec tunnel configuration context.
Configure IKE
sonic(config-ipsec-<name>)# ike crypto alg {des iv64|des|3des|rc5|idea|cast|blowfish|3idea|des iv32|null|aes cbc|aes ctr|aes gcm 16} crypto alg size <0-65535> integ alg {none|md5 96|sha1 96|des mac|kpdk md5|aes xcbc 96|md5 128|sha1 160|cmac 96|aes 128 gmac|aes 192 gmac|aes 256 gmac|hmac sha2 256 128|hmac sha2 384 192|hmac sha2 512 256} dh {none|modp 768|modp 1024|modp 1536|modp 2048|modp 3072|modp 4096|modp 6144|modp 8192|ecp 192|ecp 256|ecp 384|ecp 512|modp 1024 160|modp 2048 224|modp 2048 256}Parameters: – crypto alg: Encryption algorithm – crypto alg size: Key length in bits (0-65535) – integ alg: Integrity/authentication algorithm – dh: Diffie-Hellman group for key exchange
Configure IKE Identity
sonic(config-ipsec-<name>)# ike local type {ip4|ip6|rfc822|fqdn} data <value>
sonic(config-ipsec-<name>)# ike remote type {ip4|ip6|rfc822|fqdn} data <value>Configure Shared Key
sonic(config-ipsec-<name>)# shared key mic {string|hex} <value>Configure Traffic Selector
sonic(config-ipsec-<name>)# ike traffic selector local ip4 addr start <ip> addr end <ip>
sonic(config-ipsec-<name>)# ike traffic selector remote ip4 addr start <ip> addr end <ip>Defines which traffic should be encrypted.
Configure SA
sonic(config-ipsec-<name>)# sa {des iv64|des|3des|rc5|idea|cast|blowfish|3idea|des iv32|null|aes cbc|aes ctr|aes gcm 16} crypto alg size <0-65535> integ alg {none|md5 96|sha1 96|des mac|kpdk md5|aes xcbc 96|md5 128|sha1 160|cmac 96|aes 128 gmac|aes 192 gmac|aes 256 gmac|hmac sha2 256 128|hmac sha2 384 192|hmac sha2 512 256}Configures Security Association parameters.
Configure SA Tunnel
sonic(config-ipsec-<name>)# sa tunnel {ip4|ip6} src ip <a.b.c.d> dst ip <a.b.c.d> next hop <a.b.c.d> remote ip <a.b.c.d/m> shared interface <interface>Parameters: – src ip: Local tunnel endpoint – dst ip: Remote tunnel endpoint – next hop: Gateway to reach remote peer – remote ip: Protected remote network – shared interface: Physical interface carrying tunnel traffic
Advanced SA Settings
sonic(config-ipsec-<name>)# sa init
sonic(config-ipsec-<name>)# sa lifetime <value> jitter <value> handover <value> max bytes <value>
sonic(config-ipsec-<name>)# sa natt {enable|disable}Parameter Explanation: – lifetime: SA validity duration (seconds) – jitter: Random variation to prevent simultaneous rekeying – handover: Overlap time for smooth SA transition – max bytes: Data limit before rekeying – natt: NAT traversal support
Bind IPSec to Interface
sonic(config)# interface ethernet <id>
sonic(config-if-<id>)# ipsec <name> peer {ip4|ip6} <address>Show Commands
sonic# show ipsecDisplay IPSec tunnel information.
Troubleshooting
Tunnel Won’t Establish
Symptom: IPSec status shows “down” or “no SA”
Checks:
1. Verify network connectivity between peers:
ping <remote-peer-ip>2. Check IKE configuration matches on both sides:
show ipsec3. Verify pre-shared key is identical (case-sensitive):
show run | grep "shared key"4. Ensure traffic selectors match:
- Local traffic-selector on Device1 = Remote traffic-selector on Device2
- Remote traffic-selector on Device1 = Local traffic-selector on Device2
5. Check firewall rules allow UDP 500 (IKE) and UDP 4500 (NAT-T)
Traffic Not Encrypted
Symptom: Tunnel is up but traffic flows unencrypted
Checks:
- Verify traffic selectors include target networks
- Ensure NAT is not interfering:
show nat translations3. Check routing – traffic must be routed through tunnel
Performance Issues
Symptom: Slow throughput over tunnel
Solutions:
1. Enable NAT Traversal:
sonic(config-ipsec-<name>)# sa natt enable2. Adjust MTU (try 1400 or lower):
sonic(config-if-2)# mtu 14003. Use hardware-accelerated encryption (AES-NI on x86)
4. Consider tuning SA lifetime for less frequent rekeying
Common Error Messages
| Error | Cause | Solution |
| IKE authentication failed | Pre-shared key mismatch | Verify identical keys on both sides |
| No proposal chosen | Crypto parameters mismatch | Ensure identical algorithms and key sizes |
| Traffic selector mismatch | Subnet configuration error | Verify traffic selectors are reciprocal |
| Packet fragmentation detected | MTU too high | Reduce MTU to 1400-1492 |
Security Best Practices
Encryption Strength
Recommended Settings:
# Strong encryption with AES-256
ike crypto alg aes cbc crypto alg size 256 integ alg hmac sha2 256 128 dh modp 4096
# Or use AES-GCM for combined encryption+authentication
ike crypto alg aes gcm 16 crypto alg size 256 integ alg none dh modp 4096Avoid Weak Algorithms:
- ❌ DES, 3DES (deprecated)
- ❌ MD5 (vulnerable to collisions)
- ❌ DH groups below modp-2048
Key Management
1. Use strong pre-shared keys:
- Minimum 20 characters
- Mix of uppercase, lowercase, numbers, symbols
- Generate with:
openssl rand -base64 32
2. Rotate keys periodically:
- Change pre-shared keys every 90-180 days
- Use different keys for different tunnels
3. Protect configuration files:
# Restrict access to running-config
chmod 600 /etc/sonic/config_db.jsonMonitoring & Logging
Enable IPSec logging:
sonic(config)# logging server <syslog-ip>
sonic(config)# logging level ipsec debugMonitor tunnel health:
# Set up periodic checks
sonic(config)# ip sla 1
sonic(config-sla-1)# icmp-echo <remote-subnet-ip>
sonic(config-sla-1)# frequency 60Support & Resources
Need hardware for your deployment? Check out AsterNOS-VPP compatible hardware:
- ET2508 Gateway/Router – 50Gbps IPSec throughput
- ET3608 Gateway/Router – 80Gbps IPSec throughput
- ET3616 Gateway/Router – 2x 80Gbps IPSec throughput
Or download the free version for x86 platforms and test in your lab environment!
